January 2022
Sci Transl Med.
Mitochondrial-cell cycle cross-talk drives endoreplication in heart disease
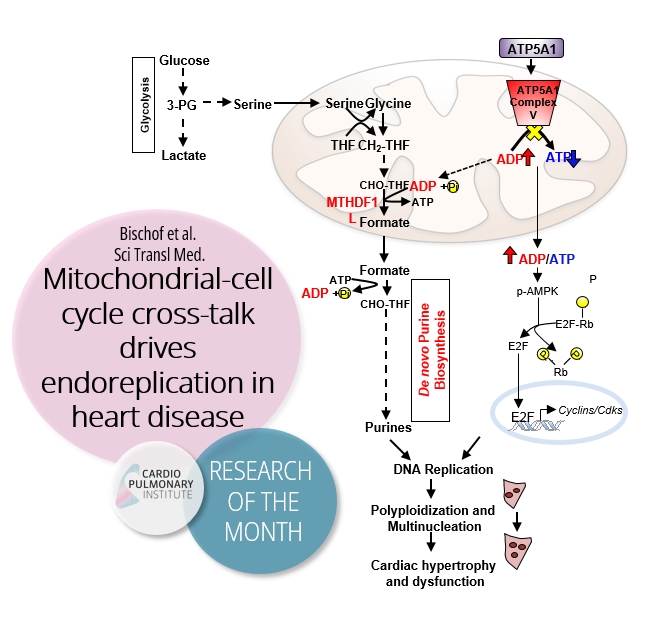
Figure 1: Mechanism of F1F0 ATP synthase function in cardiac ploidy and growth control.
Pathologic stress leads to the decreased expression of the alpha subunit of F1F0 ATP synthase (ATP5A1). As a consequence of F1F0 ATP synthase inhibition, the ADP/ATP ratio is elevated inside the mitochondrial matrix which, on one hand, activates the energy sensor AMPK. pAMPK in turn hyperphosphorylates Rb resulting in the release of the transcription factor E2F and induction of cyclins and CDKs expression. On the other hand, the accumulating mitochondrial ADP is rechanneled towards MTHFD1L, an enzyme involved in the mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism that uses ADP as a cofactor to catalyze the conversion from CHO-THF to formate. Formate, that is particularly derived from serine, serves as a 1-carbon donor for the de novo synthesis of purines. The increased de novo formation of purines as substrates for nucleic acid synthesis and the induction of cyclins and CDKs promote DNA replication, multinucleation and cardiac growth. CHO-THF denotes formyl-tetrahydrofolate, CH2-THF denotes methylenetetra-hydrofolate, 3-PG denotes 3-phosphoglycerate.
Original publication: